Introduction: The Rise of Telemedicine and Remote Health Monitoring
Telemedicine and remote health monitoring technologies have dramatically transformed the healthcare landscape, offering patients and providers unprecedented convenience, efficiency, and accessibility. These innovations not only streamline the healthcare process but also reduce the burden on traditional healthcare systems by eliminating some of the most common inefficiencies, such as long wait times and high costs.
Telemedicine, which allows patients to consult with healthcare providers via video calls, phone consultations, or online messaging, has seen rapid adoption over the past decade. Coupled with health monitoring devices like wearables, telemedicine is expanding the scope of healthcare services, making them more affordable and accessible. This article explores the profound impact telemedicine and health monitoring systems have on patient care, how they address long-standing issues in the healthcare system, and the future of healthcare in a digital-first world.
1. The Basics of Telemedicine and Remote Health Monitoring
Before delving into the impact of telemedicine and health monitoring, it is essential to define these technologies and understand how they function in modern healthcare systems.
Telemedicine: A New Era in Patient-Provider Interaction
Telemedicine involves using telecommunications technology to provide clinical services remotely. This can include:
- Video consultations: Patients meet with their healthcare providers via video calls, enabling face-to-face interaction without leaving their homes.
- Phone consultations: For more straightforward consultations or follow-ups, patients can speak to their doctors over the phone.
- Text or email-based consultations: Some medical professionals offer consultations through secure messaging or email for non-urgent issues.
Telemedicine has expanded the reach of healthcare services to remote, underserved areas, making it possible for people in rural or isolated regions to access medical advice without the need for travel.
Remote Health Monitoring: Aiding in Preventive Care and Chronic Condition Management
Remote health monitoring refers to the use of wearable or home-based devices to track a patient’s vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, and oxygen saturation. Devices such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, blood pressure monitors, and glucometers can continuously monitor health metrics and send real-time data to healthcare providers.
- Wearable devices: Track physical activity, sleep patterns, heart rate, and more. Examples include the Apple Watch, Fitbit, or Garmin devices.
- Medical-grade devices: These include tools like home ECG monitors or blood pressure cuffs that send data directly to healthcare providers for more accurate and timely interventions.
These technologies allow for early detection of potential health issues, better chronic disease management, and overall improved patient outcomes by offering continuous and proactive care.
2. Reducing Waiting Times: Immediate Access to Care
One of the most significant advantages of telemedicine and remote health monitoring is the ability to eliminate long wait times, which have traditionally been a major barrier to timely healthcare.
Streamlined Consultations
Telemedicine eliminates the need for patients to physically visit a healthcare facility, significantly reducing wait times for appointments. This is especially beneficial for individuals in urgent need of care or for those dealing with routine consultations, such as medication refills or follow-up visits after a procedure.
- Example: Patients no longer need to take time off work or travel long distances to see a doctor. Instead, they can simply schedule a video call from home, often receiving consultation within a few hours.
Enhanced Scheduling Flexibility
By using virtual consultation platforms, healthcare systems can streamline their scheduling processes. Doctors and patients alike benefit from greater scheduling flexibility, with no need for time-consuming back-and-forth phone calls to find available slots.
- Example: A virtual consultation system can automatically synchronize the doctor’s availability with the patient’s, offering a more convenient experience for both parties.
Reducing Emergency Room Overcrowding
Telemedicine helps reduce overcrowding in emergency rooms by enabling patients with non-urgent conditions to receive immediate care from home. This also allows healthcare workers to focus on patients with more critical needs, optimizing the overall flow of care.
- Example: Patients with minor health complaints, such as colds, rashes, or ear infections, can opt for telemedicine consultations instead of visiting the ER or urgent care centers, which helps reduce the strain on physical healthcare facilities.
3. Cutting Healthcare Costs: A More Affordable Option
Traditional healthcare visits can be expensive, with patients often paying for consultations, transportation, and sometimes extended hospital stays. Telemedicine and health monitoring offer significant cost-saving benefits for both patients and healthcare providers.
Reduced Travel and Transportation Costs
Patients no longer need to drive long distances or take public transportation to see a doctor. This not only saves money on fuel, parking, and transit costs but also eliminates time lost in traffic or waiting in crowded waiting rooms.
- Example: Rural residents, who might have to drive for hours to reach the nearest healthcare facility, can instead consult with doctors remotely, cutting down on travel expenses and time spent.
Lower Consultation Fees
Telemedicine consultations often cost less than in-person visits. Since healthcare providers do not need to maintain physical office spaces or pay for utilities and office staff, the overall cost of providing care is reduced, resulting in lower consultation fees for patients.
- Example: A standard telemedicine consultation can be significantly cheaper than an in-person appointment, especially when the visit doesn’t require any physical examination or specialized medical equipment.
Fewer Missed Appointments and Follow-ups
Remote health monitoring enables ongoing care without the need for frequent office visits. By tracking patients’ conditions in real time, healthcare providers can detect early warning signs of problems and take proactive action, potentially preventing costly complications down the road.
- Example: A patient with hypertension who wears a home blood pressure monitor may only need to visit their doctor every few months rather than having to make frequent trips for blood pressure checks. This reduces both direct and indirect healthcare costs.
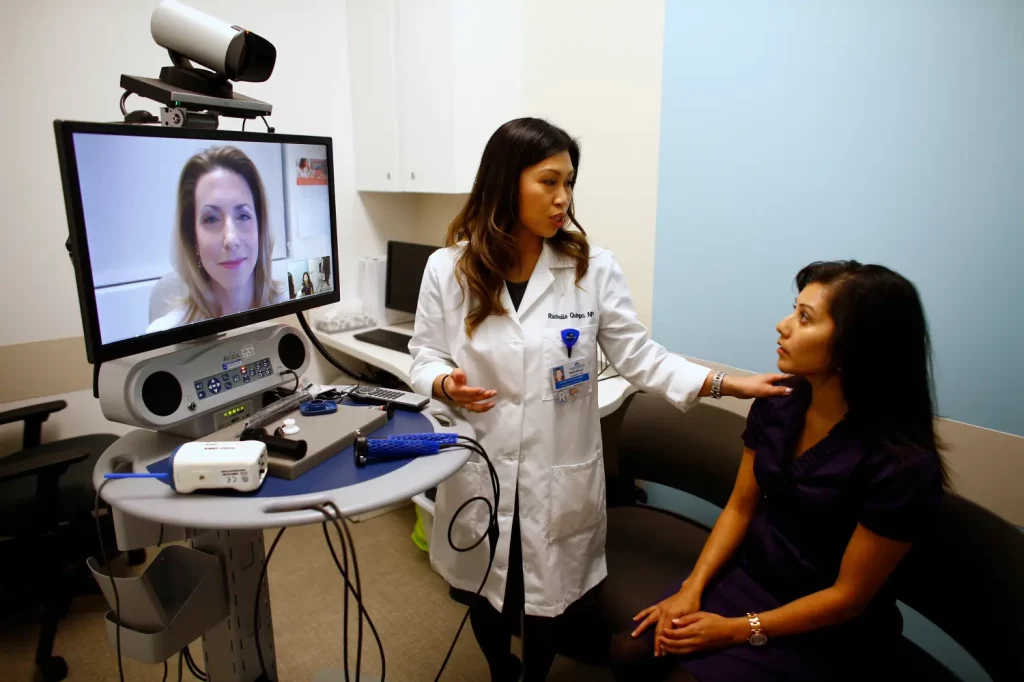
4. Expanding Access to Healthcare: Bridging the Gap
Telemedicine and remote health monitoring technologies are playing a crucial role in expanding healthcare access, particularly for individuals in underserved or hard-to-reach areas.
Reaching Rural and Remote Communities
In many rural or underserved regions, access to healthcare professionals can be limited due to geographic isolation or a shortage of healthcare providers. Telemedicine provides an effective solution, allowing patients in remote areas to access quality care without traveling long distances.
- Example: In rural areas of countries like the United States, India, and Africa, telemedicine has been instrumental in providing healthcare to people who would otherwise have to travel hours to see a doctor.
Bringing Specialist Care to the Masses
Telemedicine is also a game-changer for accessing specialist care. In many locations, specialized doctors or medical professionals are few and far between. Telemedicine bridges this gap by allowing general practitioners to consult with specialists remotely, ensuring that patients receive the care they need without having to travel for specialist appointments.
- Example: A general practitioner in a small town can connect with a cardiologist or neurologist in a major city to consult on the best treatment plan for a patient, enhancing the patient’s care without needing them to travel.
5. Improving Patient Outcomes through Continuous Monitoring
Remote health monitoring empowers patients and healthcare providers with real-time health data, enabling more accurate diagnoses and timely interventions, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
Proactive Care for Chronic Conditions
Chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and asthma require ongoing monitoring. Remote health monitoring tools allow patients to manage their conditions better by providing continuous data that is transmitted to healthcare providers, who can then make adjustments to treatment plans as needed.
- Example: A diabetic patient using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) can receive real-time feedback on their blood sugar levels. The data is shared with their healthcare provider, who can make immediate adjustments to the patient’s insulin regimen or dietary plan, reducing the risk of complications.
Early Detection of Health Issues
Regular monitoring of vital signs can detect early signs of health problems before they become serious. For example, a wearable device might pick up irregularities in heart rate, prompting a healthcare provider to investigate further, leading to early intervention.
- Example: An ECG monitor detects irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia) in a patient, leading to an early diagnosis and timely treatment, preventing potentially fatal complications like stroke or heart failure.
6. The Future of Telemedicine and Health Monitoring
The future of telemedicine and remote health monitoring is bright, as new technologies continue to emerge that will further enhance the delivery of healthcare services.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning will further improve telemedicine by enabling more personalized healthcare. AI can analyze patient data to predict health outcomes, recommend preventive measures, and even assist in diagnostic procedures.
- Example: AI-powered tools can help doctors analyze imaging data or interpret test results, leading to faster and more accurate diagnoses, while telemedicine platforms can provide tailored health advice based on individual health histories and preferences.
Telemedicine for Mental Health
Telemedicine is also expanding into mental health services, allowing individuals to consult therapists, counselors, and psychiatrists remotely. This is particularly beneficial for those who experience stigma surrounding mental health or have difficulty accessing mental health services.
- Example: Online therapy platforms like BetterHelp or Talkspace enable individuals to receive counseling from licensed professionals through video calls or secure messaging, increasing accessibility to mental health care.
7. Conclusion: A More Efficient, Affordable, and Accessible Healthcare System
Telemedicine and remote health monitoring have revolutionized healthcare by reducing waiting times, lowering costs, and expanding access to care. These technologies facilitate more personalized, proactive care while improving patient outcomes and making healthcare more efficient. As the world moves toward a digital-first approach to healthcare, these innovations will continue to shape the future of patient care, making healthcare more accessible, affordable, and effective for everyone.
By leveraging these technologies, we are not only improving the quality of life for patients but also building a more sustainable and equitable healthcare system for the future.











































